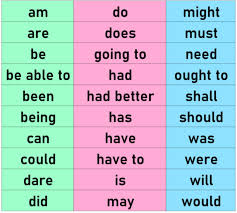
Auxiliary verbs or helping verbs, are verbs that are used in conjunction with a main verb to form a verb phrase. They help to take additional information about the action expressed by the main verb, such as tense, temperament, voice, or characteristic.
The primary auxiliary verbs are:
- Be (is, are, am, was, were, being, been)
- Have (have, has, had, having)
- Do (do, does, did, doing)
primary auxiliaries, there are also modal auxiliary verbs, which express requirement, opportunity, agreement, or skill. Some common modal auxiliary verbs are:
- Can
- Could
- May
- Might
- Must
- Shall
- Should
- Will
- Would
For example:
- She is running. In this sentence “is” is the auxiliary verb that helps to show the present continuous tense of the main verb “running.”
- They can swim. In this sentence “can” is the modal auxiliary verb that shows skill.

Types of Auxillary Verbs:
Auxiliary verbs are divided into two main types:
1- Primary auxiliary verbs
2- Modal auxiliary verbs.
1. Primary Auxiliary Verbs
Primary auxillary verbs are used to form different tenses, characteristics, and voices of main verbs. There are three primary auxiliary verbs in English:
- Be:It is used to form continuous tenses and the passive voice.
- Example: “He is jumping.” (present continuous)
- Example: “The book was written by her.” (passive voice)
- Have: It is used to form perfect tenses.
- Example: “We have finished our homework.” (present perfect)
- Example: “I had left before she arrived.” (past perfect)
- Do: It is used to form questions, negatives, and definite speeches.
- Example: “Do you like tea?” (question)
- Example: “I do not remember.” (negative)
- Example: “I do want to go!” (emphasis)
2. Modal Auxiliary Verbs
These verbs express requirement, oportunity, aggrement, skill, or obligation. Some common modal auxiliary verbs are:
- Can:It shows skill or opportunity.
- Example: “she can cook
- Could:It showsA past ability or polite needs.
- Example: “Ali could play the guitar when he was younger.”
- May: It shows agreement or option.
- Example: “she may leave early.”
- Might:It shows a weaker possibility.
- Example: “It might rain later.”
- Must:It shows obligation or strong obligation.
- Example: “He must wear a seatbelt.”
- Shall:It Often used to indicate future act or to make suggestions .
- Example: “We shall return.”
- Should: Shows advice or approval.
- Example: “You should see a doctor.”
- Will:Shows future aim or willingness.
- Example: “Youiwill help me.”
- Would: Used for polite needs or imaginary conditions.
- Example: “I would like a cup of tea.”
Examples:
Example sentences for both primary and modal auxiliary verbs, along with their functions:
Primary Auxiliary Verbs
| Auxiliary Verb | Example Sentence | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Be | She is cooking. | Forms the present continuous tense. |
| Have | We have finished our homework. | Forms the present perfect tense. |
| Do | Do you like tea? | Forms a question. |
| I do not remember. | Forms a negative statement. | |
| I do want to go! | Adds emphasis to the main verb. |
Modal Auxiliary Verbs
| Modal Verb | Example Sentence | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Can | She can swim. | shows skill. |
| Could | He could play the piano when he was younger. | shows past ability. |
| May | You may leave early. | shows aggrement. |
| Might | It might rain later. | shows a weaker possibility. |
| Must | she must wear a seatbelt. | Shows necessity or strong obligation. |
| Shall | we shall return. | Indicates future act |
| Should | she should see a doctor. | shows advice or approval. |
| Will | You will help me. | showss future intention or willingness. |
| Would | I would like a cup of tea. | Used for polite requests or imaginery conditions. |
These examples express how auxiliary verbs function in sentences to caary different meanings and grammatical structures.